A Safety Management System (SMS) needs to maintain a comprehensive safety-related database that can provide the essential and foremost components of Safety analysis. The safety-related data can be obtained from various sources that experts often consider to have a causal relationship with the prevailing safety condition. The various safety data can be considered in the Safety Management System including police reported crash records, citations record sets. Being part of an integrated asset management system, SMS also has access to roadway attributes from MIRE element data. Once data is available in the system, a Safety Analyst conducts a systematic analysis to identify the locations where safety interventions may have the most effective outcome in terms of reduction in crashes. This systematic process is referred to as network screening.
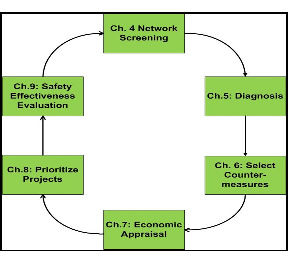
Network screening is the process of identifying and ranking high crash locations on a highway network. These sites are likely to experience a reduction in crash frequency with the implementation of countermeasures. The flow diagram for the Safety Management System is shown in Figure 1 below. In the life cycle of safety management, the first and foremost step is to perform network screening. Every highway agency needs to screen their network to identify the high crash locations so that further Diagnosis can be carried out to identify the safety issues and appropriate countermeasures.
In Safety Analyst, the process of network screening can be summarized as follows:
- Identify the analysis scope (i.e. define network) and choose the screening methods (refer to Setup>Profile Management)
- Calculate the selected performance measure (e.g. Fatal crash count, Type A crash count, etc.) (refer to Hotspot Rule)
- Execute the screening scenario.